{Achieving stringent demands regarding subzero processes necessitates expert valve system. Our organization’s cryogenic 3-way spherical component alternatives are fabricated to provide unwavering performance even at very low temperatures, typically below -150°C. These mechanisms offer superior stream regulation in frozen materials such as nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, frequently applied in sectors like LNG, research equipment, and healthcare facilities. We specialize in strong construction, including low-friction fastening constituents and careful fabrication, to ensure hermetic working. Consider the gains of enhancing your freezing system with our cutting-edge 3-way orbital valve solutions.
Exceptional Twin Seal and Vent Rotational Valve Packages
In terms of vital systems, particularly where leakage is disallowed, exemplary double block and bleed sphere valves offer unparalleled protection. This groundbreaking design incorporates two separate seal valve seals, consequently a bleed opening, allowing for authentication of the whole shut-off and finding of any possible fluid loss. Regularly employed in fuel workflows, synthesis processing, and low-temperature locations, these systems markedly elevate functional protection and lessen the probability of habitat influence.
Three-Directional Sub-Zero Orbital Valve Architecture
A design of three-port glacial globular valve presents a peculiar engineering issue. These devices are regularly employed in important industrial implementations where drastic heat levels must be preserved. Key issues include ingredient option, particularly regarding delicacy at diminished chills, and the must for sealed locking to prevent draining of frosty fluids. Intricate analysis strategies and detailed manufacturing steps are essential to warrant dependable effectiveness and longevity under such rigorous engaging circumstances.
Glacial Valve Behavior in Commercial Applications
This demanding prerequisites of ice-cold services, such as supercooled natural petroleum handling and subzero nitrogen storage, necessitate robust control device techniques. Integral block drain instruments provide a particularly robust and effective procedure to achieving zero-leak closure while facilitating frequent maintenance. Their design incorporates a primary assembly with a small purge corridor, allowing managed pressure relief during termination and resumption. This inherent aspect minimizes remaining material entrapment, thereby ensuring paramount defense and performance even under the most unyielding running conditions. Furthermore, the capability to assess drain discharge provides valuable diagnostic statistics for procedure advancement.
Attaining 3-Way Globular Valve Barrier in Extreme High-Pressure Scenarios
Ensuring stable tightness performance with 3-way sphere valves becomes particularly vital when operating within marked pressure situations. The design should account for significant burdens and potential oozing pathways. Specialized components, often including advanced metals like rust-resistant steel or exotic alloys, are mandatory to cope with the extreme conditions. Furthermore, intricate interface geometries and careful construction processes are imperative to minimize flow and guarantee a leak-proof union even under fluctuating stress cycles. Regular examination and scheduled care programs are as well vital for durability and persistent operational efficiency.
Freezing Ball Valve Leakage Prevention Strategies
Decreasing "oozing" from cryogenic "ball valves" demands a multifaceted "technique". Initial "blueprint" considerations are paramount; material "decision" must account for extreme "climatic conditions" and potential embrittlement, often favoring materials like stainless steel or specialized alloys. Beyond "compound", meticulous "manufacturing" processes – including stringent weld "reviews" and non-destructive "examination" – are vital to ensure structural integrity and eliminate voids that could become "channels". A "decisive" component is proper "installation"; thermal "contraction" during cooldown can induce stresses, necessitating careful alignment and support. Furthermore, regular "repair" – including periodic "supervision" for signs of wear and "fixing" of any identified issues – is indispensable for maintaining a reliable, leak-tight "lock”. Ultimately, a robust "structure" incorporating these elements is necessary to ensure the safe and efficient "operation" of cryogenic systems reliant on these valves. Failure to address these concerns can lead to product "depletion", safety "perils", and costly "cessation”.
Dual Stopper and Discharge Mechanism Review Procedures
To secure the integrity and safety of critical piping structures, rigorous parallel block and discharge apparatus assessment operations are essential. These tests, often mandated by regulatory bodies and industry best procedures, typically involve simulating simultaneous closure of two isolation devices while simultaneously ensuring the bleed component remains functional and correctly discharges any trapped commodity. A common mode is to utilize a pressure test where the system is pressurized to its maximum working pressure, and the spillage rate around the closed devices is meticulously appraised. The escape instrument's effectiveness is then confirmed by verifying its ability to relieve pressure. Proper documentation of assessment results, including any outliers observed, is indispensable for maintaining a reliable function.
Perceiving Integral Block Bleed Apparatus Effectiveness
For successfully regulate stress assemblies, a in-depth comprehension of integral block discharge device functionality is undeniably imperative. These specific elements principally work to reliably vent superfluous load from a system during defined working stages. A typical placement embraces a fitted compartment joined to the primary force source, permitting particular led emission if obligatory. The fundamental plan decreases the possibility of surge pressure, safeguarding both the devices and the nearby surroundings. Regular examination and repair are indispensable to secure peak capability.
Electing the Suitable 3-Way Ball Valve for Cryogenic Fluids
Identifying a fitting 3-three-ball gate for cryogenic functions demands careful assessment of several critical features. The extremely low cold states inherent in cryogenic systems – often plummeting to -196°C (-321°F) or lower – present special challenges. Material determination is paramount; only materials with proven correspondence and ductility at these temperatures, such as durable steel grades like 304L or 316L, or specialized copper alloys, should be examined. Furthermore, the device's sealing functionality is vital to prevent spillages, requiring unique stem sealing formations and low-temperature substances. Finally, pressure scales and actuation ways, taking into account potential pressure peaks, must be meticulously matched to the system's needs. Neglecting these points can lead to severe failure and safety risks.
Frostbitten Rotary Valve Component Matching Manual
Identifying the appropriate component for cryogenic circular valves is paramount, given the harsh temperatures involved. This guide highlights common components and their conduct when exposed to cryogenic fluids such as coolant nitrogen, compound helium, and oxygen. Stainless steels, particularly forms 304 and 316, often demonstrate adequate resilience and corrosion resistance, though martensitic substances require careful consideration regarding fragility. Aluminum alloys can be suitable for certain applications, however, their bendability and immunity to specific chemicals needs intensive evaluation. Copper alloys, while offering some advantages, may exhibit lowered functionality at these minimized temperatures. Consultation with providers and comprehensive assessment is essential to ensure continuity and dependability in cryogenic applications.
Increasing Double Seal and Release Installation Efficiency
Gaining optimal performance in double block and bleed arrangements hinges on a multifaceted strategy. Careful analysis of component selection is vital, with a focus on component suitability and load classification. Regular supervision of discharge ways for blockage is urgent, often entailing the use of precise analysis instruments. Furthermore, practice modernization—including inspection of circulation rates and pressure divergence—can dramatically elevate overall system steadiness and defense. Finally, adherence to vendor instructions and the deployment of a solid overhaul timetable are vital for long-term reliability and stability.
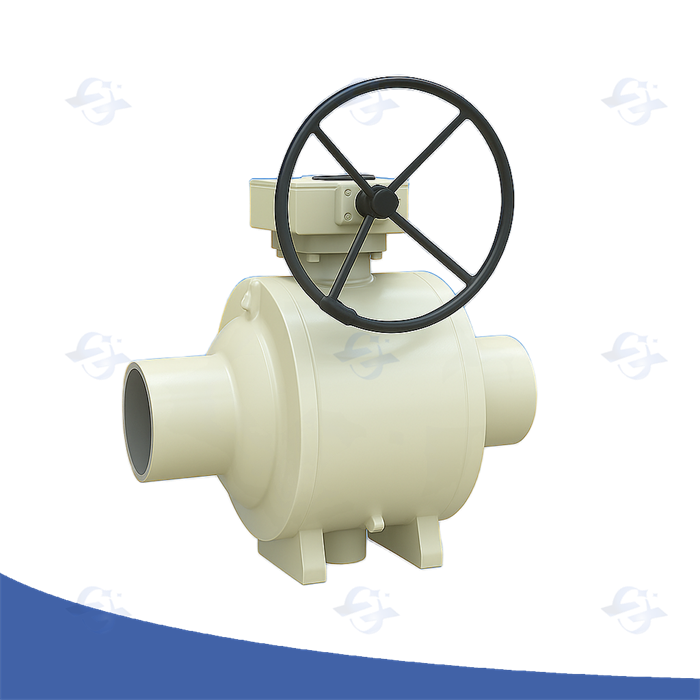 Integral Block Bleed Valves
Integral Block Bleed Valves